Wi-Fi vs. Ethernet: Which Connection to Use?

There’s no doubt that the world is moving towards wireless technologies. Such technologies provide the convenience of connecting to the internet from anywhere.
Thus, WiFi is the first choice for anyone who intends to connect to the internet and get online.
The development of more and more IoT apps means that we’ll be seeing a large number of smart devices in our homes and offices very soon – devices that connect to the internet and work wirelessly.
You can also use Ethernet from WiFi. For this, you must know how to convert a WiFi signal to an Ethernet connection
Does all this advancement in IoT application development and wireless technologies mean that the time of Ethernet is over? Or do you think that traditional wired cable connections will continue being used to go online?
In this article, we’ll explore the main differences between Ethernet and Wifi connections. You’ll also learn which connection is best for your needs.
Some of the main points covered in this article are:
- What is WiFi?
- What is Ethernet?
- Ethernet vs. WiFi
- Speed
- Reliability
- Security
- Latency
- Interference
- Portable devices
What is WiFi?
WiFi is a wireless technology that connects devices to the internet without any physical wired connection. Introduced in 1999, it is the most popular type of connection used today.
What is Ethernet?
Introduced in 1973, Ethernet is a way of connecting devices in a LAN. Consisting of an Ethernet cable, hub, crossover cable and router, it enables devices to transmit data over a network.
Ethernet vs. WiFi
If the question was asked some time ago, the answer would be a bit different than it is today. Because Ethernet uses cables, it tends to work slightly faster than a wireless connection.
Wireless connections are a bit slower, but provide the convenience of using it within range. Today, WiFi hotspots can easily be found in many places.
Thus, the choice lies between speed and convenience.
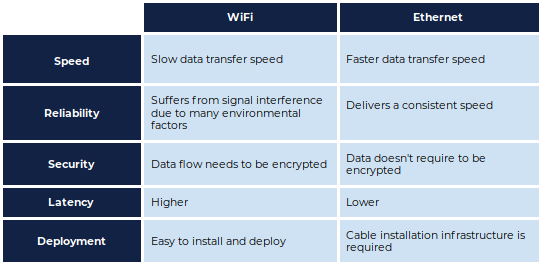
Speed
WiFi was initially based on the 802.11g standard. The maximum theoretical speed was 54Mbps.
Mobile phones could be connected to the internet with this connection, but the speed was much slower when compared to Ethernet – which could easily provide 100Mbps-1,000Mbps and beyond.
802.11ac is the latest WiFi standard, offering speeds of up to 3,200Mbps. With this new standard, WiFi is in much better standing next to Ethernet in terms of speed.
Reliability
The speeds discussed above are theoretical.
An Ethernet connection delivers a consistent speed. You’ll notice this fast and stable speed if you download large files. Ethernet connections are also suitable for streaming HD videos.
WiFi suffers from signal interference due to many environmental factors. The atmosphere can cause issues, and WiFi often produces inconsistent performance. You’ll observe sporadic signaling when you move from one place to another in your home. This issue can be minimized by placing your router in an optimum position in your home or office, but it’s still challenging to achieve the same stable performance of Ethernet connections.
Security
This is another primary factor.
Data sent over an Ethernet connection can only be accessed by devices that are physically attached to that network, and thus there is no chance of data loss or hacking.
These devices need to use a firewall for their security.
WiFi, on the other hand, is an open network so its data isn’t safe. When transmitting sensitive data, be sure to use WiFi networks where the data is encrypted is secured. The most secure encryption method is the WPA2-PSK, while WEP is the least secure.
Free public WiFi is the most unsecure. Learn more about its privacy pitfalls here
Latency
Connection speed and quality are not the only things to consider – latency matters, too.
Latency is the delay with which traffic travels from a device to its destination. Also referred to as a ping in the online gaming world, latency is vital when playing games. Reaction time must be quick, and the same goes in the IoT data world.
If you want to avoid irritating lags or delay while posting data, then an Ethernet connection is the right choice.Wired connections offer lower latency.
Interference
We have many devices in our home or offices that can interfere with WiFi, causing various problems.
These issues include:
- Dropped signals
- Greater latency
- Lower speeds
Thus, Ethernet is more reliable in terms of interference.
Portable Devices
Obviously, no one’s connecting their smartphones to the Ethernet.For portable or remote devices, WiFi is the clear first choice.
Which Connection to Choose?
- If you want a connection for everyday use, then an adequately configured WiFi router will give you a suitable connection.
- But if you’re a gamer and can’t risk an unstable connection, you’ll want to go with Ethernet.
- Similarly, if you need to stream HD videos without issue, or connect several devices to your network, you’ll undoubtedly see better performance with an Ethernet connection.
Wireless routers also have Ethernet ports so you can configure devices individually without any issues.
Final Words
Both WiFi and Ethernet have their pros and cons. These depend on several factors like interference, medium standard, protocol standard, latency, etc. WiFi is more popular these days, but Ethernet connections still offer some significant benefits. As such, you should choose your connection based on your needs.
If you found the post useful and you wish to learn more about both WiFi and Ethernet, make sure to share it with all your friends and check out Ubidots, the simple yet powerful IoT platform that allows you to gather data from any device connected to the Internet. Until then, happy browsing!