5 Essential Modbus Sensors for Industrial Automation (With Examples)
Here's a list with five types of Modbus-compatible sensors that can have a profound impact on different industrial operations and a featured example for each of them.

In the world of industrial automation, sensors play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling various processes. They provide essential data that helps in making informed decisions to enhance efficiency, safety, and productivity. One of the most popular protocols for communication with sensors is Modbus. This article goes over the Modbus, the RTU and TCP versions of the protocol, and highlights five types of Modbus-compatible sensors that can have a positive impact in different kinds of operations.
What is Modbus?
Modbus is a serial communication protocol developed by Modicon in 1979 for use with its programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It has since become a standard in industrial communication systems. Modbus allows for communication between multiple devices connected to the same network, such as sensors, actuators, and controllers.
Modbus RTU
Modbus RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) is the most widely used version of Modbus. It operates over serial communication lines like RS-485 or RS-232. The RTU format includes a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) for error checking, ensuring reliable data transmission. It is particularly favored for its simplicity and robustness in harsh industrial environments.
Modbus TCP
Modbus TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is a variant that operates over Ethernet. This allows for faster data transfer rates and the ability to integrate with modern networking equipment. Modbus TCP is beneficial in environments where high-speed communication and remote access are required.
» FREE TRIAL: Embrace the digital transformation and drive up efficiency in your operation with Ubidots
Being a long-standing and reputable protocol, there are all kinds of sensors that are compatible with Modbus and Modbus networks. However, based on our experience at Ubidots and hand-on tests, we decided to make a list with five types of Modbus-compatible sensors that can have a profound impact on different industrial operations and a featured example for each of them.
1. Modbus Energy Meters
Power measurement sensors are crucial for monitoring electrical parameters such as voltage, current, power factor, and energy consumption. These sensors help in managing power usage efficiently and detecting anomalies that could indicate equipment failure or energy wastage.
Impact of Power-Related Issues
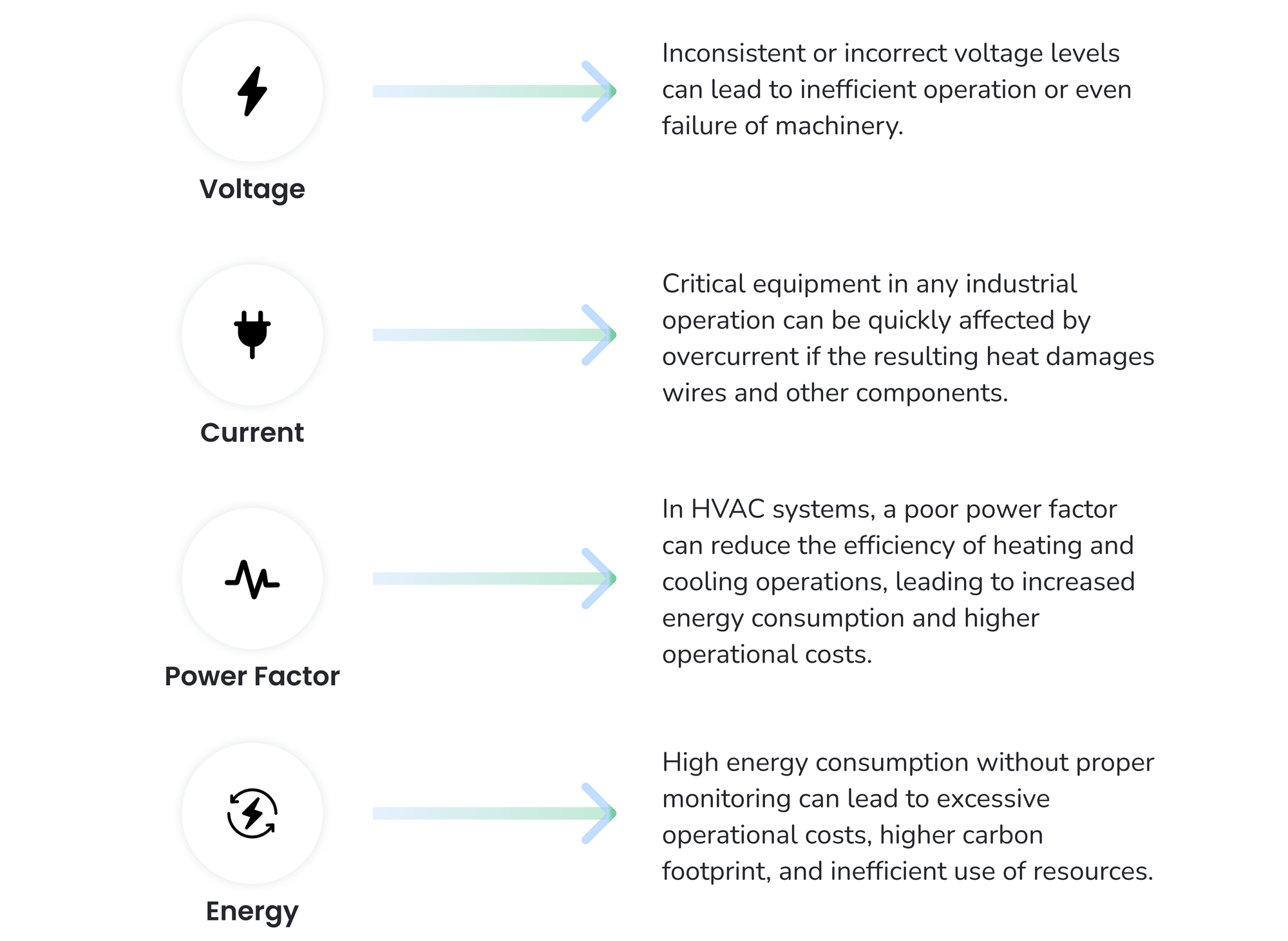
- Voltage:
- Industrial Processes: Inconsistent or incorrect voltage levels can lead to inefficient operation or even failure of machinery. Overvoltage can damage sensitive equipment, such as control systems and computers, while undervoltage can result in inadequate performance and increased wear and tear on motors and other components. This can cause significant downtime, reduce productivity, and increase maintenance costs.
- Current:
- Industrial Equipment: Critical equipment in any industrial operation can be quickly affected by overcurrent if the resulting heat damages wires and other components. Apart from heat, the powerful magnetic fields caused by the overcurrent can also place a lot of stress on the equipment, even warping them out of shape.
- Power Factor:
- HVAC Systems: In HVAC systems, a poor power factor can reduce the efficiency of heating and cooling operations, leading to increased energy consumption and higher operational costs.
- Energy Consumption:
- In Any Type of Operation: High energy consumption without proper monitoring can lead to excessive operational costs, higher carbon footprint, and inefficient use of resources.
Understandably, monitoring these power-related variables can bring benefits such as the following:
- Energy Optimization: By monitoring power usage, businesses can identify areas where energy is being wasted and implement measures to optimize consumption. This leads to more efficient operations and reduced energy costs.
- Reliability: Ensuring stable power supply and proper operation of electrical systems increases the reliability of industrial processes and minimizes disruptions.
- Extended Equipment Life: Proper power monitoring helps prevent conditions that can damage equipment, extending its lifespan and reducing the frequency of replacements and repairs.
- Risk Mitigation: Monitoring power parameters helps in early detection of potentially hazardous conditions like overcurrent, overvoltage, and short circuits. This allows for timely intervention to prevent accidents and ensure safety.
- Compliance: Adhering to electrical safety standards is important to meet different regulations that are common around the world. Power measurement can help you avoid legal issues thanks to timely reactions.
Featured Power Device: 3-Phase Power Measurement Module
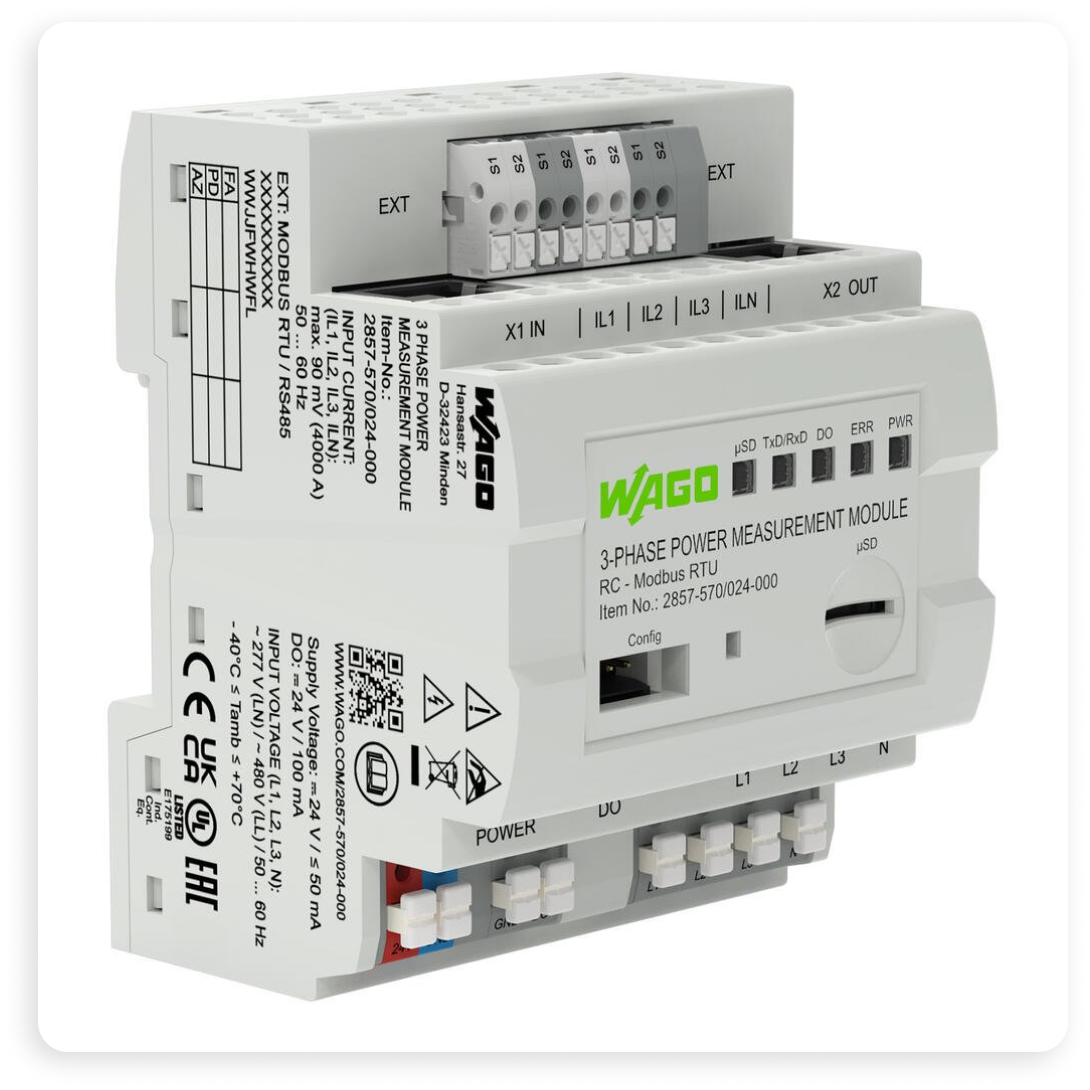

WAGO's 3-Phase Power Measurement Module is a versatile and compact device designed for measuring electrical data in three-phase supply networks. Housed in a DIN-rail-mount enclosure, this module provides remote monitoring capabilities from the control level, making it ideal for various industrial applications. The module measures critical electrical variables, including active, apparent, and reactive power, energy consumption, power factor, phase angle, and frequency.
One of the standout features of WAGO's module is its ability to store measured variables on a microSD card, facilitating mobile measurement and data logging. The device supports current measurement via a 1A current transformer and includes a configurable digital signal output for pulse output. Additionally, it offers a configuration interface for displaying and configuring measured values during operation, ensuring ease of use and flexibility.
2. Modbus Flow Meters
Modbus flow meters are essential in various industries such as water treatment, chemical processing, oil and gas, and food and beverage. These sensors can measure either the volumetric or mass flow rate of a fluid moving through a pipe, providing critical data for process control and optimization. Volumetric flow meters measure the volume of fluid per unit time, while mass flow meters measure the mass of fluid per unit time. Density flow meters, although not measuring flow rate directly, are often used in conjunction with flow meters to provide density data that can be used to calculate mass flow from volumetric flow measurements.
Understanding how flow and density measurement impacts industrial processes and other operations can help in achieving higher efficiency, quality, and safety.
How Flow and Density Problems Impact Operations
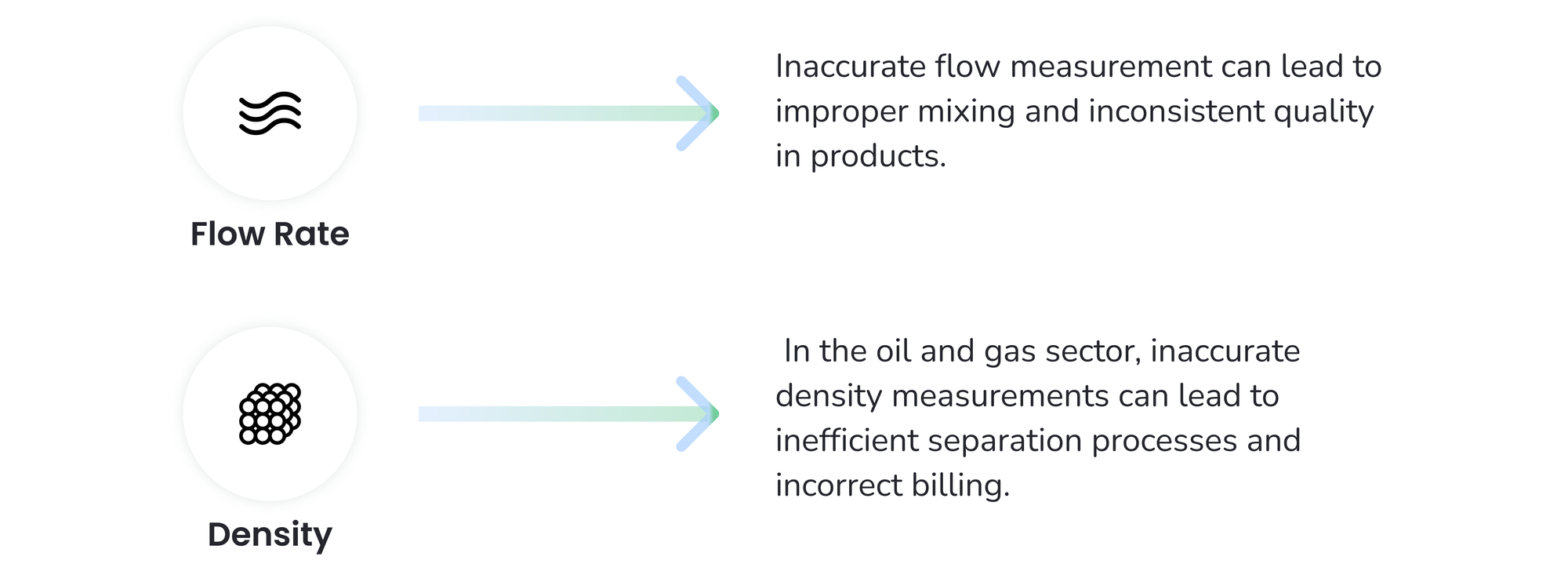
- Flow Rate Issues:
- Industrial Processes: Inaccurate flow measurement can lead to improper mixing and inconsistent quality in products. For instance, in the chemical industry, incorrect flow rates can result in the wrong proportions of reactants, producing off-specification products that may need to be reprocessed or discarded, thereby increasing operational costs and waste.
- Water Treatment: In water treatment plants, improper flow measurement can affect the dosing of chemicals, leading to either under-treatment or over-treatment of water. This can result in unsafe water quality, regulatory fines, and increased operational costs.
- Greenhouses: In greenhouses, improper irrigation due to inaccurate flow measurements can lead to either water stress or waterlogging in plants, affecting their growth and yield. Over-irrigation can also waste water resources and increase costs.
- Density Issues:
- Food and Beverage Industry: Incorrect density measurements can lead to inconsistent product quality, affecting taste, texture, and overall consumer satisfaction. For example, in dairy processing, variations in milk density can impact the consistency and quality of products like cheese and yogurt.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In the oil and gas sector, inaccurate density measurements can lead to inefficient separation processes and incorrect billing. This can result in significant financial losses and disputes with customers or suppliers.
Being able to detect flow and density issues early, or prevent them altogether, has these benefits and more:
- Consistency: Monitoring flow and density ensures consistent product quality by maintaining the correct proportions of materials. This is particularly important in industries where precise formulations are crucial, such as pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
- Resource Management: Efficient flow and density control minimize the use of raw materials and reduce waste, leading to cost savings and more sustainable operations.
- Predictive Maintenance: Anomalies in flow and density measurements can indicate potential issues with equipment, such as blockages or leaks. Early detection allows for preventive maintenance, reducing unexpected downtime.
- Environmental Protection: Accurate measurements help in controlling emissions and discharges, reducing the environmental impact and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Featured Flow Device: Rosemount 3418
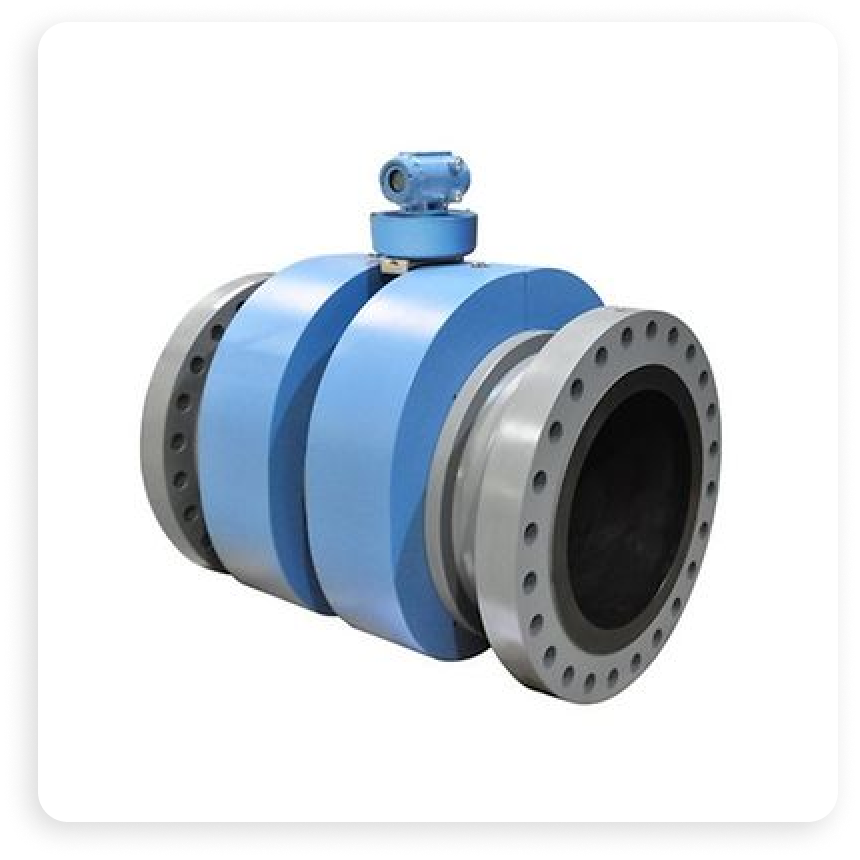

Emerson's Rosemount 3418 8-path ultrasonic flow meter offers the highest levels of accuracy and performance for sophisticated fiscal measurement applications. The Rosemount combines the power of two interlocked 4-path British Gas design meters into a single flow meter body. This innovative configuration features a mirror image of the first set of chords, effectively canceling out the effects of swirl and cross flow. With an impressive 0.5 OIML accuracy class, the Rosemount 3418 requires only five diameters of straight run and eliminates the need for a flow conditioner, significantly reducing compression and pumping costs while eliminating maintenance due to blockages.
The Rosemount is packed with advanced features that enhance its functionality and ease of use. Its high rangeability of greater than 100:1 ensures fewer meter runs, smaller line sizes, and lower capital costs. Crafted from durable carbon steel and stainless steel, the Rosemount 3418 is built to withstand harsh industrial environments while delivering unparalleled accuracy and performance.
3. Modbus Ambient Sensors
Ambient sensors are essential in monitoring environmental variables such as carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, temperature, and humidity. These measurements play a critical role in various industries and applications, such as HVAC systems, greenhouses, food storage, manufacturing, and more.
Impact of Ambient-Related Issues
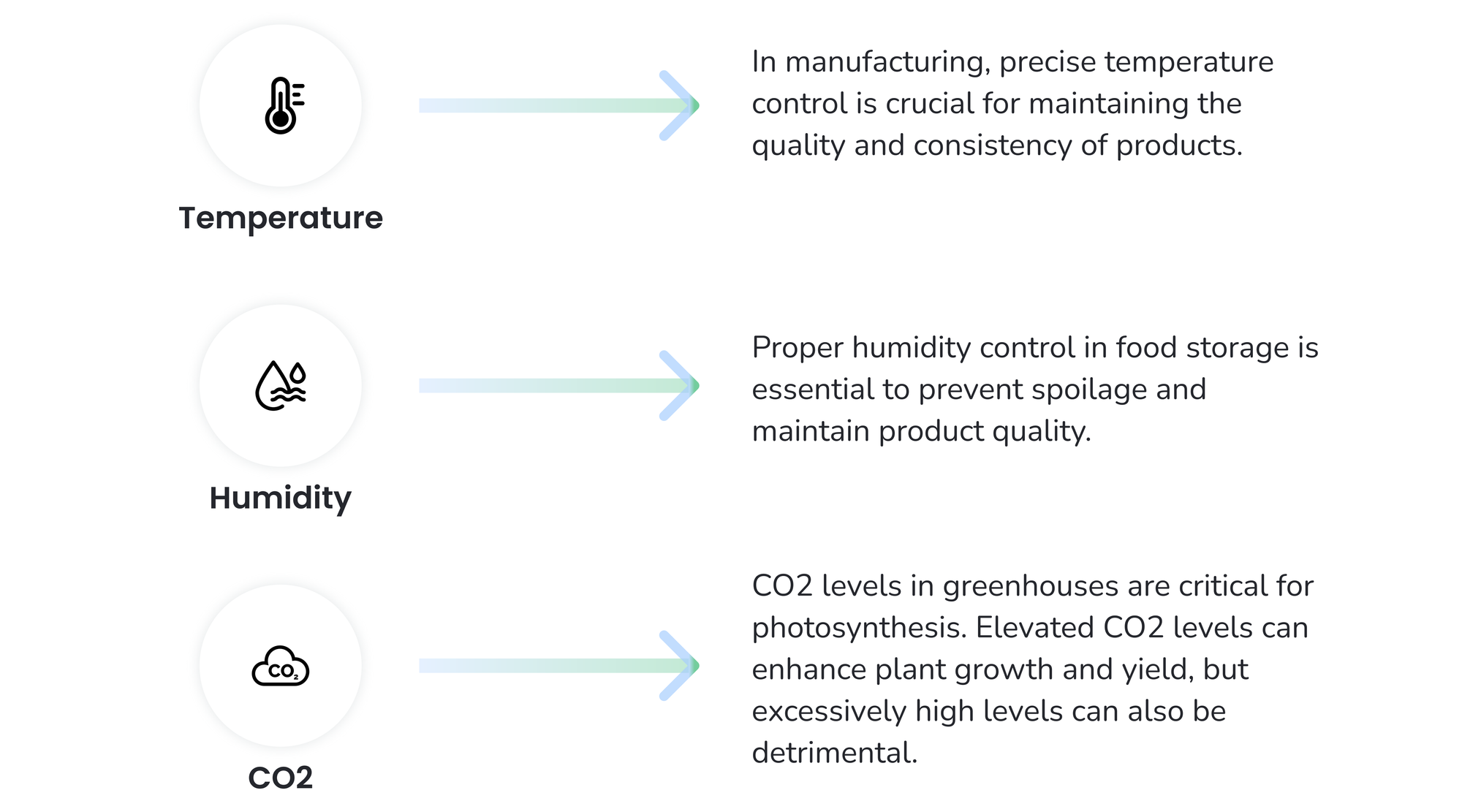
- Temperature changes:
- In industrial processes: In manufacturing, precise temperature control is crucial for maintaining the quality and consistency of products. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, temperature fluctuations can affect the stability and efficacy of drugs.
- In greenhouses: Temperature control in greenhouses is vital for the growth and development of plants. Too high or too low temperatures can stunt growth, affect flowering, and reduce crop yields.
- Humidity changes:
- In industrial processes: Humidity can significantly impact processes such as painting, coating, and printing. High humidity can cause condensation, leading to defects and poor adhesion, while low humidity can lead to static electricity issues.
- In food storage: Proper humidity control in food storage is essential to prevent spoilage and maintain product quality. High humidity can lead to mold growth, while low humidity can cause products to dry out and lose their texture.
- CO2 changes:
- In greenhouses: CO2 levels in greenhouses are critical for photosynthesis. Elevated CO2 levels can enhance plant growth and yield, but excessively high levels can also be detrimental.
- In habitability/safety: Monitoring CO2 levels in buildings and workspaces helps maintain good indoor air quality. High CO2 concentrations can lead to drowsiness, reduced productivity, and health issues.
Consequently, monitoring ambient variables and acting upon critical changes in a timely manner brings several benefits, including:
- Consistency: Monitoring and controlling ambient variables ensure consistent conditions, leading to higher product quality and uniformity.
- Compliance: In industries such as pharmaceuticals and food processing, adhering to strict environmental standards is crucial to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Resource Efficiency: Precise control of environmental variables reduces waste of raw materials and energy. For example, maintaining the right humidity levels can prevent product spoilage and reduce waste in food storage.
- Process Safety: In processes involving volatile substances, such as chemical manufacturing, controlling ambient conditions is crucial to prevent hazardous situations.
Featured CO2 Device: SenseCAP SOLO CO2 5000 – NDIR CO2 Sensor
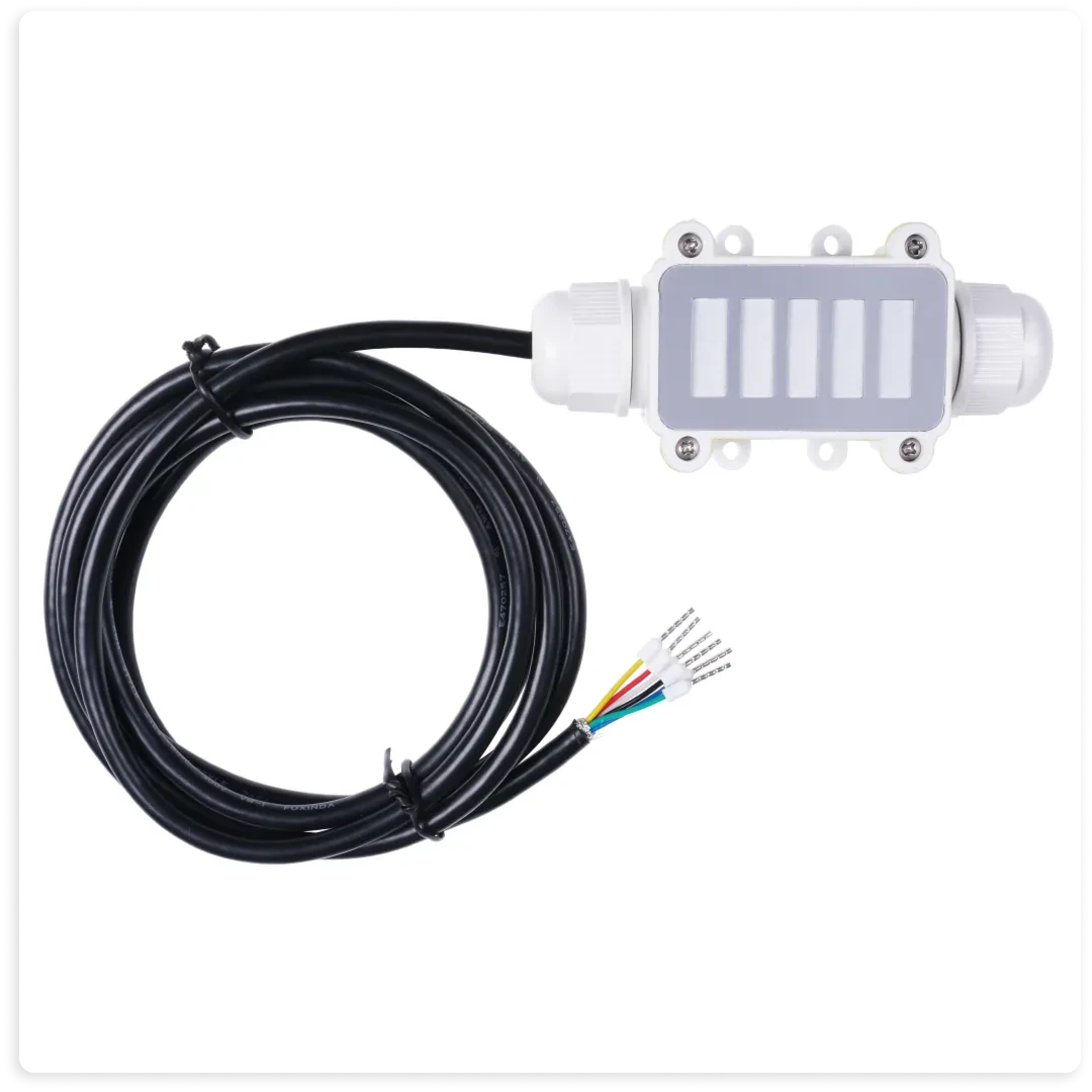

Seeed Studio's SenseCAP SOLO CO2 5000 is a high-performance NDIR CO2 concentration sensor designed for diverse applications, including greenhouses, urban environments, poultry farms, and transportation stations. Supporting Modbus (Modbus-RTU/Modbus-ASCII) RS485 and SDI-12 communication protocols, this compact sensor offers built-in calibration functionality, making it easy to integrate and operate in various scenarios where monitoring CO2 levels is critical.
The SenseCAP SOLO CO2 5000 features a wide CO2 measurement range of 400ppm to 5,000ppm with an accuracy of ± (50ppm + 5% * MV), ensuring precise and reliable data collection. Its high accuracy, fast response, and superior stability make it a dependable choice for continuous CO2 monitoring. The device supports a wide power supply range of 5V to 16V, providing flexibility in different installation environments. Its compact size and excellent performance-to-price ratio make it an ideal solution for various applications.
4. Modbus Pressure Sensors
Modbus pressure sensors, also known as Modbus pressure transmitters, are widely used in various industries to monitor and control pressure in processes involving gasses or liquids. Accurate pressure measurement is vital for ensuring safety, efficiency, and product quality.
How Pressure Problems Impact Operations
- In Manufacturing: Incorrect pressure can lead to defective products and process inefficiencies. For example, in plastic molding, incorrect pressure can result in improperly formed products, leading to high scrap rates and increased costs.
- In Food and Beverage: In the food and beverage industry, maintaining precise pressure is essential for processes like pasteurization and carbonation. Incorrect pressure can lead to spoiled products and safety hazards.
- In Filtration Systems: In water treatment plants, incorrect pressure can affect the efficiency of filtration systems. Low pressure can lead to insufficient filtration, resulting in poor water quality, while high pressure can damage filtration membranes, leading to costly repairs and downtime.
- In Drilling Operations: In oil and gas drilling, maintaining the correct pressure is critical to prevent blowouts and ensure safe operations. Incorrect pressure can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, and environmental pollution.
- Irrigation Systems: In greenhouses, pressure issues can affect the performance of irrigation systems. Low pressure can result in inadequate water supply to plants, affecting their growth and yield, while high pressure can damage irrigation equipment.
Some of the benefits of pressure monitoring include:
- Consistency: Monitoring and maintaining correct pressure levels ensures consistent product quality by enabling precise control over manufacturing and processing conditions.
- Operational Stability: Stable and accurate pressure measurements ensure smooth operation of processes, minimizing disruptions and maintaining productivity.
- Risk Mitigation: Monitoring pressure helps detect abnormal conditions that could lead to hazardous situations where equipment or processes fail. Anticipating failures with active monitoring prevent accidents.
Featured Pressure Device: Foxboro Modbus Pressure Transmitter IAP10M
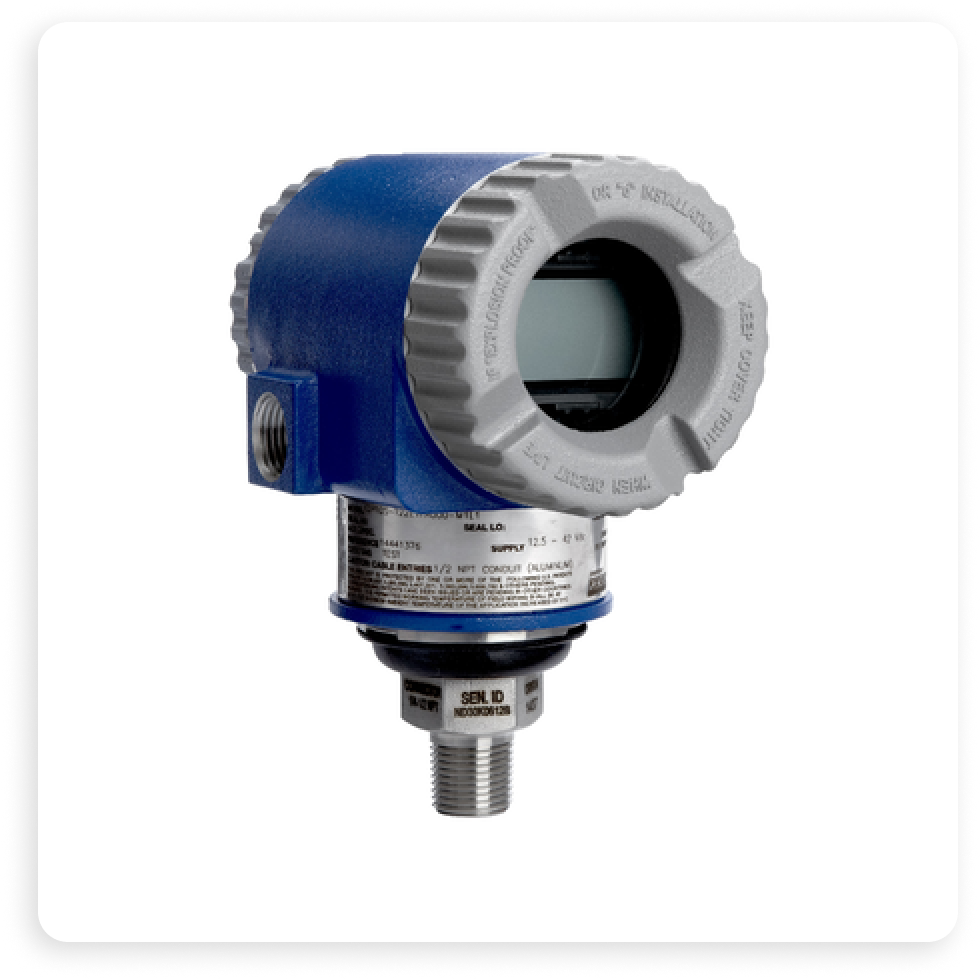

Schneider’s Foxboro Modbus Pressure Transmitter IAP10M is a highly accurate device designed for measurement of process absolute or gauge pressures. This small transmitter can be networked using Modbus over Ethernet or a selectable RS485/232 serial line, offering versatile connectivity options. Its ease of installation and operation makes it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications in the oil, gas, water, and industrial sectors.
The Foxboro IAP10M features an analog output of 0:20mA with 12-bit resolution, suitable for controlling measured variables within PID logic control at RTU. It also includes a user-friendly LCD interface with two-button control and a 2-line display featuring 13 characters for easy configuration and monitoring.
5. Vibration Measurement
Vibration sensors, also known as accelerometers, are critical in monitoring the condition of machinery and equipment in various industries. These sensors measure the vibration levels of machines, providing essential data to prevent failures, optimize maintenance schedules, and ensure smooth operations. Understanding the negative impacts of vibration problems on industrial processes and other operations highlights the importance of these sensors in achieving optimal performance and reliability.
Impact of Vibration-Related Issues
- Manufacturing: Excessive vibration in manufacturing machinery can lead to misalignment, wear and tear, and premature failure of components. This can cause production delays, reduced product quality, and increased maintenance costs.
- Machining: In precision machining operations, vibrations can lead to inaccuracies in cutting, drilling, and milling processes. This results in defective parts, higher scrap rates, and additional rework.
By monitoring vibration, you can better take care of your machines and processes achieving some benefits such as these:
- Improved Maintenance:
- Predictive Maintenance: Vibration monitoring enables predictive maintenance by identifying early signs of wear and potential failures. This allows for timely maintenance, reducing unexpected breakdowns and associated downtime.
- Extended Equipment Life: By detecting and addressing vibration issues early, the lifespan of machinery and components can be significantly extended, reducing the frequency and cost of replacements.
- Cost Savings:
- Reduced Downtime: By preventing unexpected failures through early detection of vibration issues, businesses can minimize costly downtime and maintain consistent production schedules.
- Higher Safety:
- Risk Mitigation: Monitoring vibration helps detect conditions that could lead to catastrophic failures, such as bearing failure or structural fatigue. This ensures the safety of personnel and equipment.
Featured Vibration Device: QM30VT2
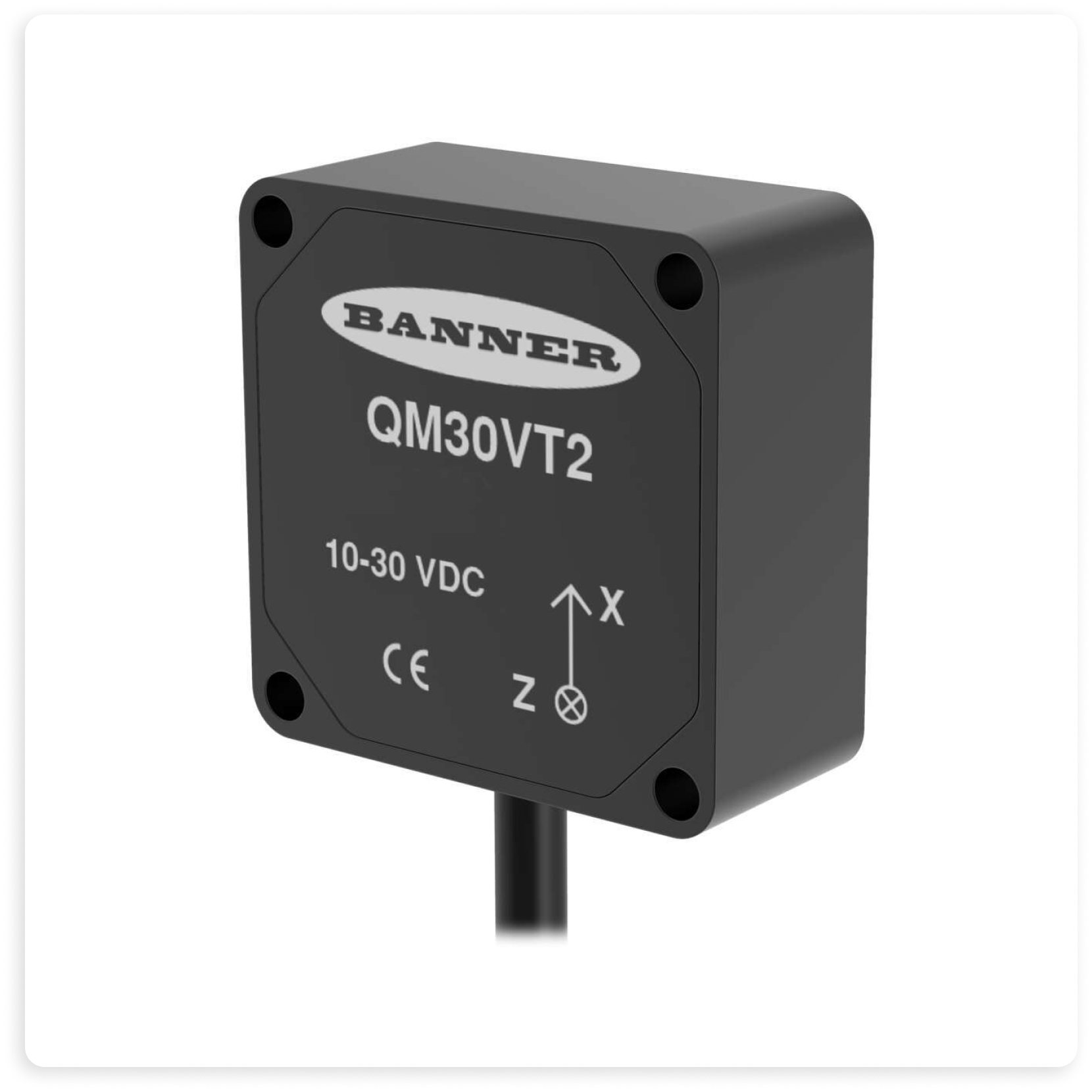

Banner’s QM30VT2 sensors offer an exceptional level of accuracy in measuring RMS velocity and temperature thanks to their design with a low-profile and rigid metal construction that minimizes resonant interference and enhances surface contact. These sensors can detect even slight increases in machine vibration and temperature, providing early identification of potential problems.
The QM30VT2 communicates performance data using Modbus RTU and is ideal for detecting potential problems in motors, fans, pumps, and any machinery with rotating motion or vibration. Available in models with either a 316L stainless steel housing or a heavy-duty aluminum housing, they are built to withstand harsh industrial environments.
Wrapping Up
Modbus remains a cornerstone of industrial communication, providing a reliable and flexible way to connect and control a wide range of sensors and devices. By understanding the capabilities of different Modbus sensors and enablers, such as PLCs and gateways, industries can optimize their processes, enhance efficiency, and ensure the smooth operation of their systems. Whether you are monitoring power, flow, pressure, or environmental conditions, Modbus-compatible devices offer a robust solution for your automation needs.
In industrial operations, maintaining control over those and other critical variables is essential for ensuring efficiency, safety, and product quality. The negative impacts of these variables exceeding their normal ranges can lead to significant operational disruptions, increased maintenance costs, and potential safety hazards. However, by utilizing Modbus-compatible sensors, industries can achieve precise monitoring and control over these variables, transforming potential risks into opportunities for optimization and improvement.
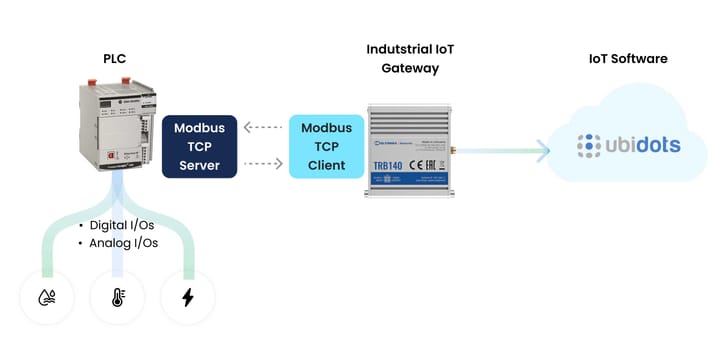
Modbus Sensors Meet the Cloud
Industrial operations around the globe are increasingly leveraging the Modbus protocol to integrate with cloud technologies by sending telemetry data to IoT platforms such as Ubidots. When paired with IoT platforms, Modbus allows real-time data from industrial processes to be transmitted to the cloud, where it can be analyzed, monitored, and controlled remotely. This integration enhances the efficiency and flexibility of industrial operations, enabling predictive maintenance, process optimization, and better decision-making through data-driven insights.
» FREE TRIAL: Embrace the digital transformation and drive up efficiency in your operation with Ubidots
How can I send Modbus sensor data to the cloud?
A Modbus network can be composed of several different types of devices, each with its own distinctive job, but the one in charge of forwarding the sensor data to the cloud is typically a gateway. Check out how you can easily send your Modbus data to the cloud by integrating your WAGO, Advantech, Red Lion (or any other) gateways to Ubidots.