How LPWANs Will Help Grow Industrial IoT

LPWAN, or low-power WAN, is a wireless wide-area network developed specifically for machine-to-machine (M2M) and the Internet of Things (IoT) networks and devices. The idea is to provide a low-bandwidth, low-cost network that exhibits a higher power efficiency than a conventional mobile one.
More importantly, LPWANs can support many connected devices over an expanded region or area when compared to traditional networks. This makes the technology ideal for something like IoT, which requires a reliable, constant and suitable connection as a means of operation. Every IoT device out there requires an active internet connection, lest they be rendered useless.
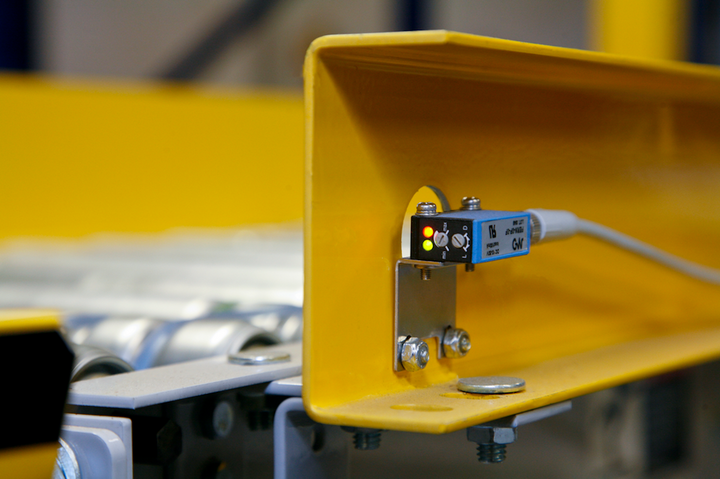
The technology can offer remarkable potential for the Industrial Internet of Things or IIoT industries, where connected devices are attached to or powering highly beneficial hardware. Manufacturing machinery, for example, might include various IoT and smart sensors, which are used to deliver real-time updates to nearby operators. Without an active connection, any data being collected and transmitted by the sensors will go nowhere.
Having an established LPWAN up and running in the area can mean the difference between a highly efficient and operational network of modern industry hardware or an ineffective and broken setup. LPWAN networks…
- expand wireless signals to greater distances,
- add stronger connections to local areas,
- and offers low-power and low-bandwidth synchronization with IoT equipment.

The nature of the technology explains why it is being hailed as a game-changer for IIoT. It will drive growth and adoption of connected systems, as well as improve the overall outlook for the entire industrial industry. More importantly, LPWANs stand to bring just about every business or organization into the modern age.
The Future of Connectivity in Industrial Settings
Devices connect to the internet in one of two ways: via a wired or wireless connection. For the longest time, if you wanted a reliable solution for connecting any equipment or hardware to the internet, wired was the way to go.
Generally, it sees a more stable connection, offers higher bandwidth opportunities and eliminates many of the troubles that go hand-in-hand with wireless networks. Blackout areas or dead zones — areas with low to nonexistent signal — are common when dealing with a wireless network.
Modern wireless technologies, however, have closed that gap between wired and wireless connection reliability. The wireless routers, hubs and network devices used to transmit a proper signal are now more powerful than ever — and that’s before you even take into account LPWAN certified tech. Many LPWAN devices access faster, LTE-capable networks that offer higher bandwidth and signal opportunities, as well as real-time connections in an unprecedented format.
Reliability, performance and usage can be enhanced even more with the adoption of cloud-based technologies. Sigfox, for instance, offers a nationwide public network, connectivity-as-a-service (CaaS) and an IoT ecosystem to meet U.S., LATAM, and European market demands.

Image source: Understanding wireless connectivity in industrial IoT applications by TI E2E Community
The technology is also still being developed and optimized, which means many new solutions will present themselves over the next few years. In fact, 57 percent of industrial IoT professionals are currently researching or actively working on industrial LPWAN solutions. Three-quarters of that audience are working on projects that target new applications, many of which cannot be addressed with conventional network tech.
All this collectively encourages growth for the industry and related platforms, resulting in greater adoption numbers for LPWAN solutions. In fact, it is one of the highest-growing technologies in the communication and IoT sector.
Over 1.1 billion IoT connections are expected to be live by 2023, with LoRa and NB-IoT technologies standing as the market leaders. That forecast can be further broken down, equaling a boon of 109 percent per year leading up to the end of 2023.
IoT will certainly become more prominent across many industries as a result, not just the industrial and manufacturing sectors.
Developing the Ideal Solution
“Anyone pursuing the ideal connectivity type must first consider the environment where your device is living as well as how large your data payload will be.” - Connectivity Now and Beyond
Low-cost, long-range technologies that support smaller payloads exist, manifested in either a LoRa or Sigfox-based solution. However, when it comes to hardware that consumes a great deal of power and requires high data rates, the tried-and-true wired connection — via Ethernet — remains one of the best options. The good news is that the technology is advancing at alarming rates, which means someday soon it may accommodate high-power, high-data-rate devices and hardware.
Better still, most IoT devices fall under the former classification, requiring little power and lower data rates, albeit with reliable bandwidth.
Any way you look at it, newer technologies such as LPWANs and more efficient data solutions like it will drive growth within industrial and manufacturing industries. The benefits and optimizations they offer are just too numerous to ignore, especially in today’s highly digital and data-centric world. LPWANs have a major role to play in IoT growth.