OEE Calculation & Monitoring: Boost Production Efficiency
Discover how real-time OEE monitoring boosts production efficiency, reduces downtime, and enhances quality with actionable insights to improve your manufacturing KPIs

In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, guessing isn’t an option. Real-time overall equipment effectiveness monitoring gives you unparalleled visibility into your production line, tracking availability, performance, and quality as they happen. Picture this: a system that flags downtime the moment it occurs, identifies speed drops instantly, and ensures every product meets your standards—all without waiting for post-shift reports. This isn’t just data; it’s actionable intelligence. By monitoring OEE in real time, you can respond to inefficiencies as they arise, minimize waste, and keep your operation running at peak efficiency. Whether it’s preventing unexpected breakdowns, fine-tuning processes, or driving consistent quality, real-time OEE monitoring transforms how manufacturers manage their production lines. The result? Faster decisions, fewer disruptions, and a production floor that’s always a step ahead.
OEE Definition: What is OEE?
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a powerful metric that measures how efficiently a manufacturing plant uses its equipment. It reveals the performance of machines by combining three critical factors: availability, performance, and quality. Availability accounts for any time lost due to equipment downtime, performance reflects the speed of operation relative to its designed maximum, and quality assesses the output that meets quality standards versus total production. These three elements work together to provide a single, actionable score—your OEE percentage—that gives insights into the true manufacturing productivity of your machinery.
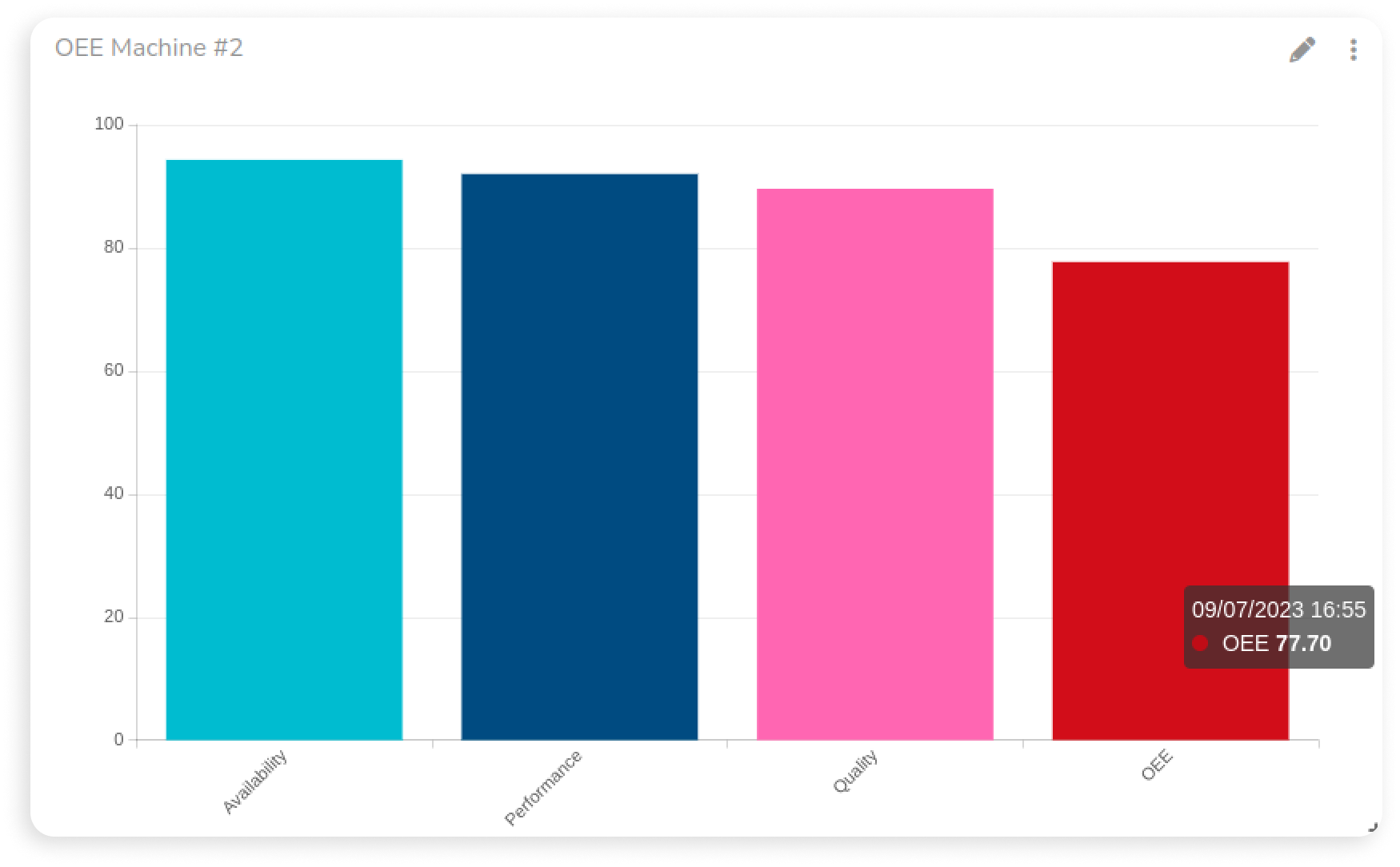
Why does overall equipment effectiveness matter? In manufacturing, efficiency isn’t just about production volume; it’s about maximizing every resource and eliminating waste. A high OEE score indicates optimal manufacturing performance, meaning machines are running smoothly, producing high-quality output, and minimizing downtime. This leads to lower operating costs, better use of raw materials, and higher profit margins. Conversely, a low OEE score signals operational inefficiencies, which could mean lost revenue, higher production costs, and possibly even missing the projected customer demand. In short, OEE isn’t just a number; it’s a snapshot of your operation's health and one of the most important manufacturing KPIs for continuous improvement. By measuring manufacturing productivity through OEE, businesses gain visibility into where they stand—and more importantly, where they can improve.
How to Calculate OEE
Measuring OEE starts by breaking it down into its three core components: Availability, Performance, and Quality. Each component addresses a specific factor of production equipment efficiency, providing a detailed view of where your manufacturing process is operating at its best—and where it may be falling short.
1. Availability:
Availability measures the uptime of your equipment, accounting for any unexpected stops or delays. It’s calculated by dividing the time your machine is actually running by the planned production time. If your equipment faces frequent stoppages, your availability score will reveal it. The formula is simple:
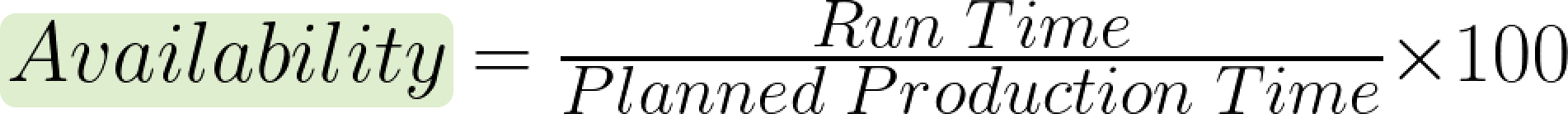
Where,
- "Run time": all the time the machines were running minus unplanned stops.
- "Planned production time": all the time the machines should ideally run for.
2. Performance:
Performance considers how fast the equipment is running compared to its maximum speed. Here, you’re not looking for just the fact that a machine is working but also if it’s working at its full potential. The performance score is calculated by comparing the actual production rate to the ideal rate:
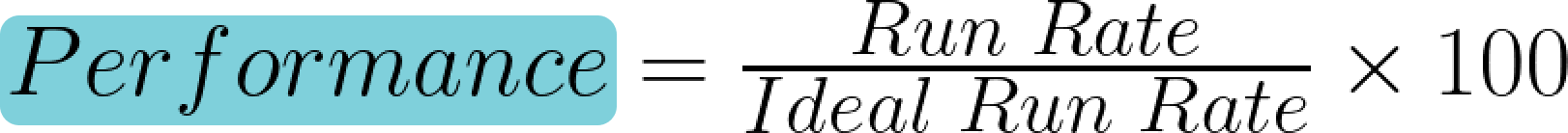
Where,
- "Run rate": rate of actual production. It is calculated by dividing the total count of produced parts by the run time.
- "Ideal run rate": maximum posible production rate.
3. Quality:
Quality zeroes in on output—specifically, how much of what you produce meets quality standards. Every product that fails inspection or doesn’t meet specifications eats away at efficiency. To determine quality, divide the number of good units by the total units produced:
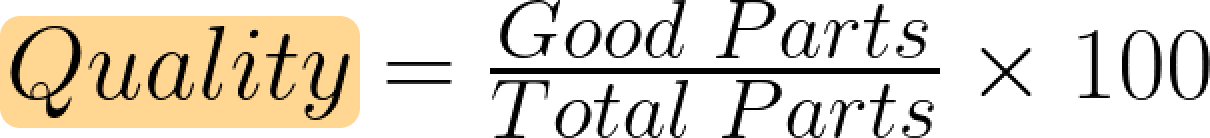
Where,
- "Good parts": total number of produced parts that pass the quality standards.
- "Total parts": total number of produced parts, including bad parts.
4. OEE
Once you’ve calculated each of these metrics, determining OEE is straightforward. Multiply the three percentages together:
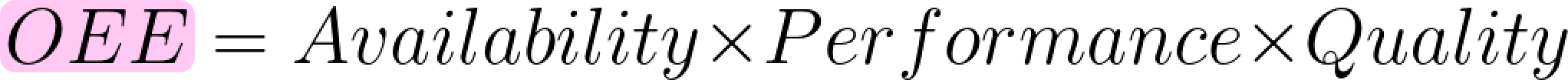
This final score, expressed as a percentage, is a clear indicator of your equipment’s overall effectiveness. A 100% OEE score signifies that the machine is running at peak efficiency with no unscheduled downtime, full speed, and zero defects. While perfection is rare, many top-performing facilities aim for 85% as an ideal benchmark.
Real Time OEE Monitoring
In the past, OEE measurement relied heavily on manual data collection and end-of-shift reports to track progress. While these methods provided basic insights, they often left critical inefficiencies unnoticed until it was too late to act. Today, manufacturing demands a more dynamic approach. Real-time OEE monitoring leverages existing infrastructure coupled with IoT sensors, and even cloud SCADAs to deliver instant, actionable insights. By tracking availability, performance, and quality in real time, manufacturers can pinpoint issues as they happen, enabling faster decisions and reducing downtime. This shift from reactive to proactive monitoring is the key to unlocking higher efficiency and staying competitive in an ever-evolving industry.
Let's dive into the practical details on how to monitor OEE in real time.
OEE Monitoring: Availability
The heart of availability's formula is the runtime. By sending a simple "status=ON" message when the machine or process is running, IoT sensors can help monitoring OEE Availability in real-time.
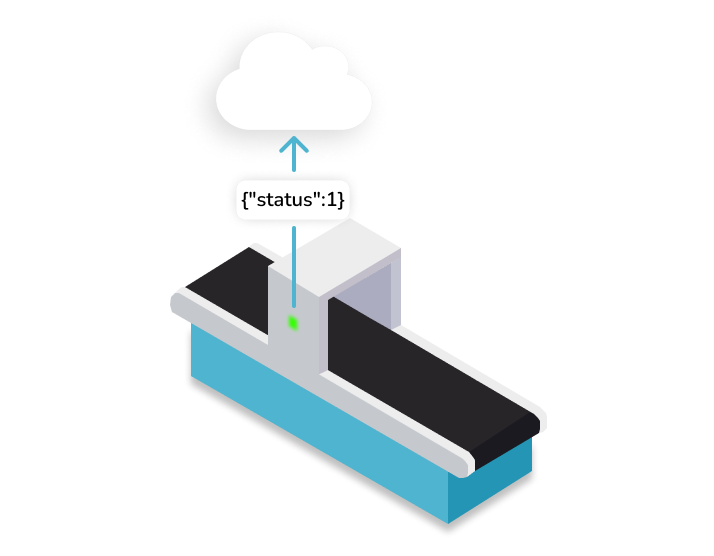
Here’s our top picks of sensors used to capture this crucial metric in real time:
- Current Sensors
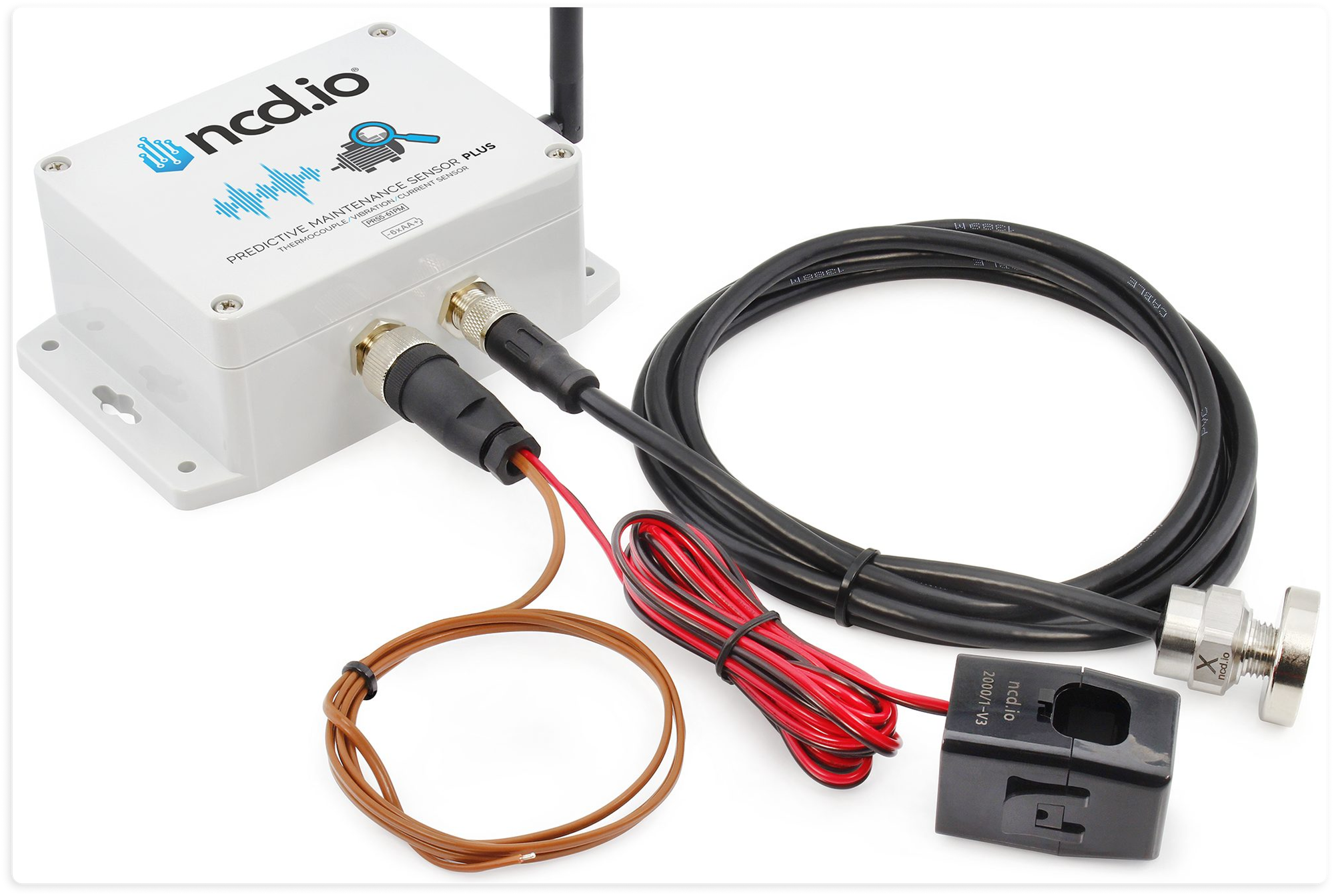
Most machinery relies on electric power, making current sensors a straightforward solution to not only measure machine usage, but also uptime. These sensors detect electric flow, a signal that, coupled with real-time monitoring tools, can be used to determine whether a machine is running or idle. By interpreting the power status, current sensors provide a reliable measure of runtime, helping identify both planned and unplanned downtimes. This continuous monitoring also ensures that you capture every minute of runtime, right down to the second, for a highly accurate availability score.

- Vibration Sensors
When it comes to rotating equipment, vibration sensors offer more than just valuable information about potential equipment failures—they can also be used to measure runtime. For equipment that runs continuously, such as motors, compressors, or pumps, vibration sensors offer an efficient, non-intrusive way to log uptime. They not only tell us when equipment is active but also provide data that could preemptively flag maintenance needs, reducing unexpected downtimes.

- PLC Data
In many cases, availability data may already be logged in Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), which track the state of machinery in real time. This can be an efficient resource to gauge truly productive manufacturing time, as most PLCs continuously log manufacturing equipment status and operational metrics. Using an IoT gateway, this data can be transmitted from PLC to the cloud, bypassing the need to install extra sensors. This option is ideal for factories equipped with a robust PLC infrastructure, as it leverages existing resources for seamless, real-time monitoring of machine runtime.
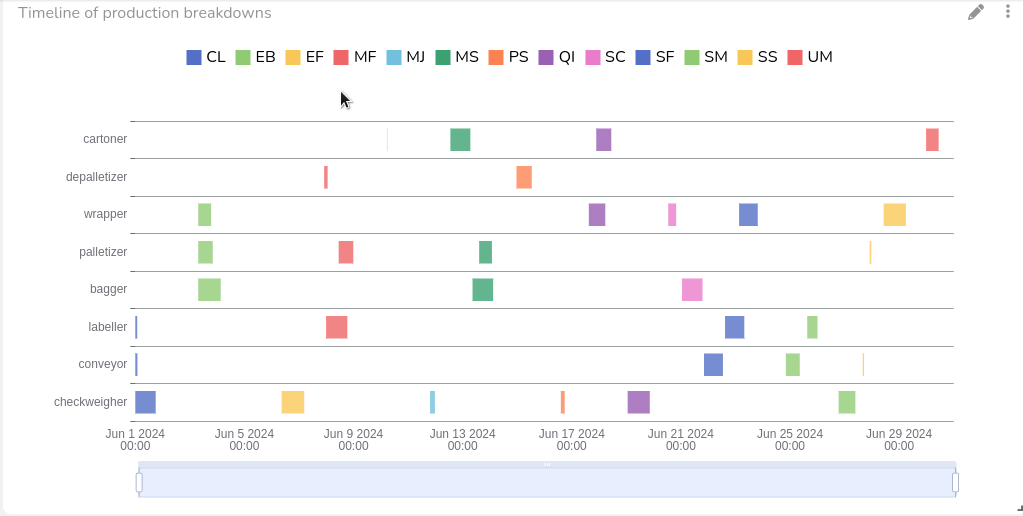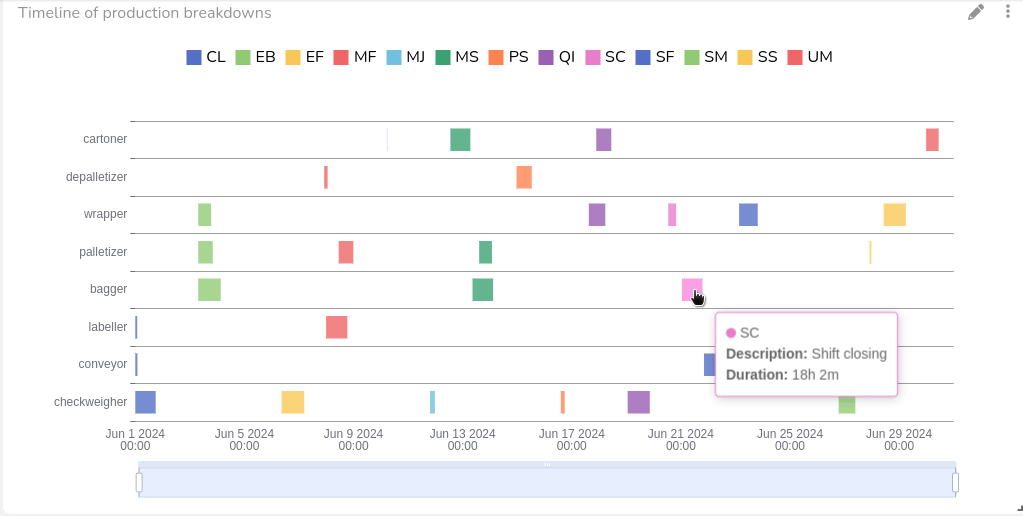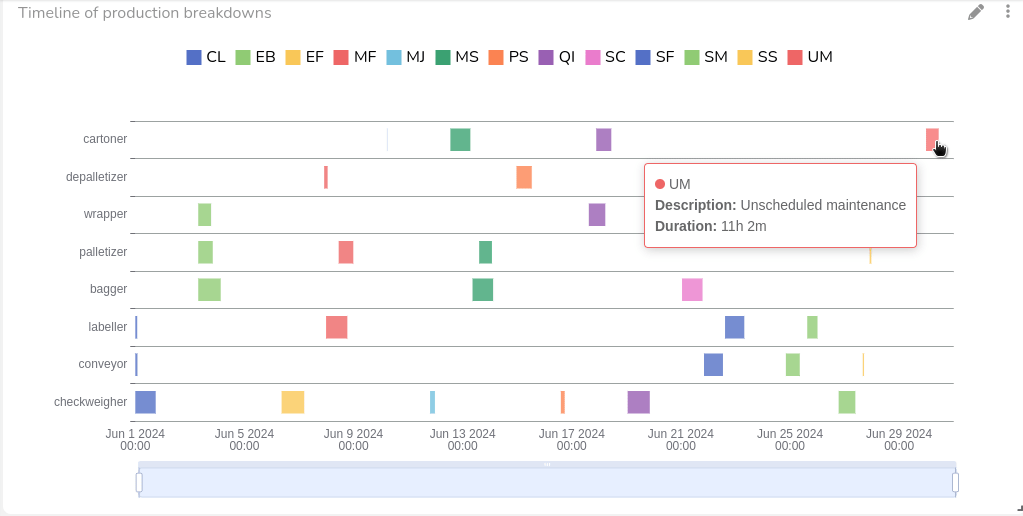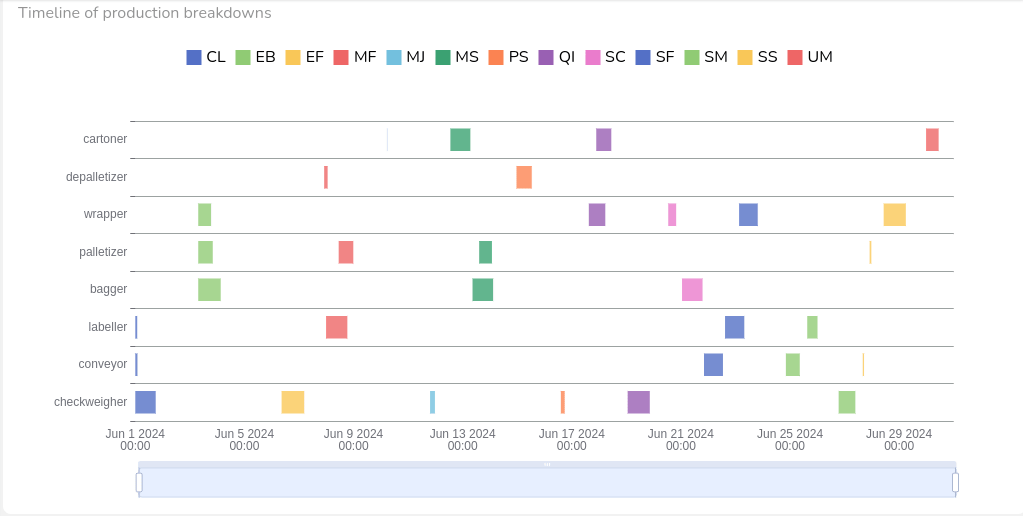
OEE Monitoring: Performance
The performance score is calculated by comparing actual production counts against the ideal, and several tools can help gather this data in real time, ensuring an accurate measure of production pace.

- Photoelectric Sensors as Counters
Photoelectric sensors are a popular choice for tracking the number of units produced. Positioned at specific points in the production line, these sensors count each unit as it passes through, providing a precise measure of output rate. For fast-moving lines or high-volume environments, photoelectric sensors are invaluable. They log each finished unit with split-second accuracy, allowing manufacturers to monitor production speed in real time and address any bottlenecks immediately.
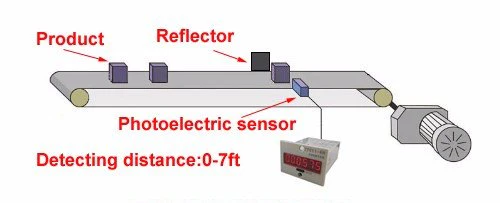
- Button Push Counter

In some manual or semi-automated production processes, especially in industries like textiles, human input still plays a role in indicating production stages. A button push counter is a simple yet effective tool in these cases. When a task or part is completed, the operator pushes a button, recording the unit’s completion. This method is particularly effective for processes that require precision or craftsmanship and may not be fully automated. By tracking each button press, you can keep tabs on production rate, allowing even manual processes to contribute to an accurate performance score.

- Contact Closure Sensors
For automated processes, contact closure sensors—also known as dry or wet contact sensors—can be a great asset. These sensors monitor the status of a relay connected to machinery, allowing you to determine whether a machine or part of a process is active. Each time the relay engages, it signals the completion of a task or cycle, providing a real-time update on production output. Contact closure sensors are effective for various manufacturing setups, from packaging lines to assembly units, where equipment activity correlates directly with production speed.
- PLC Data for Performance Tracking
As in the case of availability, performance data is already logged by PLCs in many facilities. If your production count or cycle time is recorded in PLC registers, connecting an IoT gateway to retrieve this data directly could be a good choice. It streamlines data collection without the need for extra sensors, saving both time and resources. By sending PLC data to the cloud, you can access real-time performance metrics, track trends, and quickly identify where production may be lagging.
OEE Monitoring: Quality
Unlike availability and performance, quality measurements vary significantly between industries, since each product has unique criteria that determine if it’s “OK” or “NOK” (not okay). Ensuring high quality means focusing on precision, whether it’s texture, material strength, or overall assembly. Let’s dive into some of the best tools to monitor quality in real time.
- Specialized Sensors
Different industries have different quality standards, and often, specialized sensors provide the best solution for accurate, real-time monitoring. For instance, in food production, humidity sensors are essential for maintaining the right texture in snack foods like potato chips, where moisture levels can affect crispiness. In automotive manufacturing, hardness sensors ensure each component meets rigorous durability standards. By using specialized sensors designed for specific quality factors, manufacturers can maintain a high quality rate, which translates directly into an improved OEE score.
- Smart Vision Systems
In many cases, cameras equipped with smart vision or computer vision technology offer a robust solution for quality monitoring. These systems analyze products in real time, detecting imperfections or inconsistencies instantly. For example, in electronics manufacturing, smart vision can verify component placement and solder quality, while in packaging, it ensures correct labeling and presentation. Computer vision allows for fast, detailed inspections that keep up with production speed, reducing the need for manual quality checks and minimizing error rates.
- Human Inspection with Digital Support
For products that require a more subjective assessment, human inspection remains a valuable tool. By pairing trained inspectors with digital support—such as tablets or checklists—quality assessments become more consistent and trackable. This approach is especially effective in cases where subtle details matter, like textiles, where inspectors can visually assess fabric quality or stitching. With a simple manual input widget in a tablet, operators can record "OK" or "NOK" for each product, and this data feeds directly into your OEE calculations, offering a hands-on approach to maintaining high standards.
OEE Calculation Example
Let’s walk through a real-world example to illustrate how the OEE formula can be applied in production, breaking down each step to give a clear picture of how availability, performance, and quality combine to reveal overall equipment effectiveness.
Real-World Example: Applying the OEE Formula to Production
Imagine a production line dedicated to manufacturing clay water filters. The line operates 16 hours a day, giving a planned production time of 960 minutes. Here’s the situation on a typical day:
- Availability: Due to machine adjustments and unexpected breakdowns, there are 80 minutes of downtime. This gives a runtime of 880 minutes.
- Performance: The line is monitored by a photoelectric sensor that counts the produced units. When running, the line is capable of producing 6 units per minute, so the ideal output for 880 minutes of operation is 5,280 units. However, by the end of the day, only 4,750 units were produced, showing a performance loss.
- Quality: Out of the 4,750 units produced, 4,600 pass quality control, while 150 are flagged as defective and require disposal.
Now, let’s plug these numbers into the OEE formula to see how this production line stacks up.
- Calculate Availability
Availability = (Run Time / Planned Production Time) x 100
= (880 minutes / 960) minutes x 100
= 91.66 or 91.66% - Calculate Quality
Quality = (Good Parts / Total Parts) x 100
= (4,600 / 4,750) x 100
= 96.84 or 96.84% - Calculate OEE
Now that we have each component, we can determine the overall OEE.
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
= 91.66% × 89.96% × 96.84%
≈ 79.85%
Calculate Performance
Performance = (Run Rate / Ideal Run Rate) x 100
= (4,750 / 5,280) x 100
= 89.96 or 89.96%
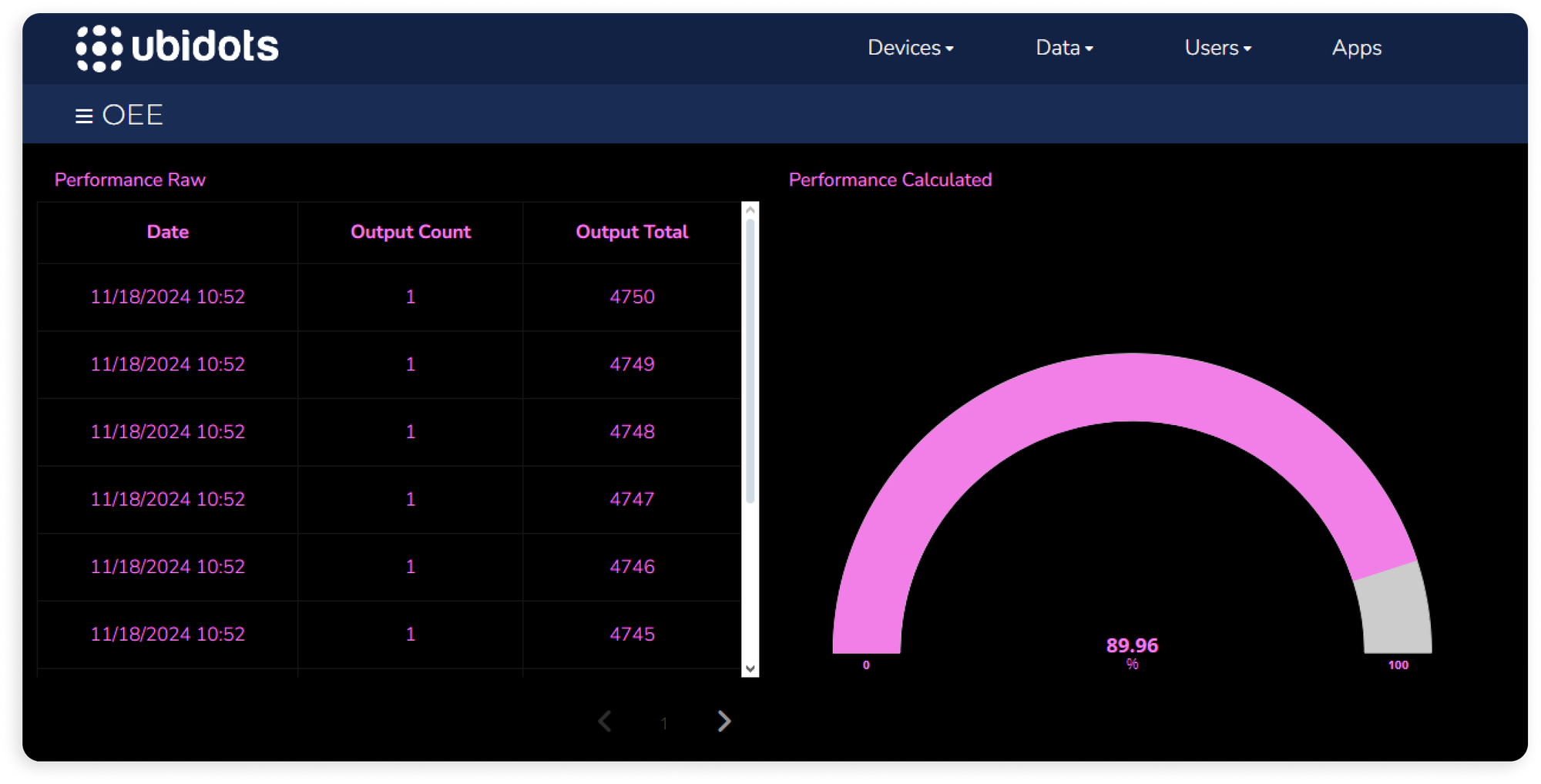
In this example, the OEE score is 79.85%. Even though a score of 79 is great already, it indicates that there’s reasonable room for improvement, particularly in availability and performance. This score shows that while the equipment produces high quality products, it’s not operational for considerable periods of the planned time and isn’t achieving the ideal production rate. By focusing on these areas, the facility could make targeted improvements to boost this score, potentially aiming for the coveted benchmark of 85% or higher.
OEE Benchmarks
OEE benchmarks serve as a reference, guiding manufacturers on where their production efficiency stands in comparison to industry standards. A high OEE score is always desirable, but what does “high” mean? For most industries, an OEE score of 85% is often considered the gold standard. This score indicates that the equipment is functioning at a high level, with minimal downtime, near-optimal performance, and a strong output of quality products. But let’s break it down further.
Industry Standards: What’s a Good OEE Score?
In practical terms, a “good” OEE score varies by industry and operational complexity. Here’s a rule of thumb:
- 50-60% OEE: Most manufacturing companies start here, facing hurdles with downtime, speed losses, or quality issues. This is an achievable baseline, but there’s room for improvement.
- 85% OEE: Top-tier performance, often seen as world-class. This is the number that most companies set as their goal. Reaching this level typically means machines run smoothly, interruptions are rare, and quality is consistently high.
- 100% OEE: Ideal, but extremely difficult to achieve in real-world conditions. Aiming for 100% is a valuable goal, but most high-performing facilities operate closer to the 85% mark.
Setting Realistic OEE Goals for Your Business
When setting OEE goals, it’s essential to focus on incremental gains. A sudden leap from 60% to 85% isn’t realistic for most operations; instead, aim for small, sustainable improvements over time. Start by targeting the biggest inefficiencies. Perhaps your equipment suffers from frequent downtime. Or maybe the machines don’t reach their full speed. Addressing these specific areas will naturally elevate your OEE score.
Aligning OEE goals with business objectives also drives a clearer path forward. Are you aiming to reduce manufacturing costs, boost output, or improve product quality? Each objective may affect how you prioritize availability, performance, and quality. For example, a company focused on rapid production may place extra emphasis on improving equipment performance, while one focused on quality control will prioritize that metric within its OEE goals.
Achieving Consistency Over Perfection
While aiming for a high OEE score is worthwhile, it’s equally crucial to focus on maintaining consistent improvements. Regularly track your OEE, spot trends, and adjust as needed. Perfection may not be achievable, but with realistic goals, continuous monitoring, and a commitment to gradual improvement, your OEE score can reflect a truly efficient, high-performing operation.
Mistakes in OEE Calculation
OEE calculations can provide valuable insights, but even minor errors in data collection or interpretation can lead to misleading results. Knowing the common pitfalls in OEE assessment helps ensure that the score you’re seeing truly reflects your production and doesn’t mask hidden inefficiencies. Here are some key missteps to watch for to maintain an accurate OEE score.
Common Pitfalls: Avoiding Errors in OEE Assessment
One of the most common mistakes is not distinguishing between planned and unplanned downtime. Planned machine maintenance or scheduled breaks, such as any changeover time, should not count against availability. When every pause, whether planned or not, is included in the runtime calculation, the availability score suffers unfairly. Ensure your data only considers unplanned downtime to keep the availability metric accurate.
Another frequent error is miscounting production speed. Often, only completed units are counted, which can overlook speed losses occurring due to minor stoppages or slowdowns. These interruptions may seem insignificant in isolation but can impact production performance over a full shift. Tracking speed losses accurately gives a truer picture of performance.
Quality measurement can also be tricky. Sometimes, defective products are not fully accounted for, particularly if they are identified and reworked later in the process. All units that fail quality inspection, even if fixed, should be recorded as defects initially. This practice ensures that your quality score genuinely reflects production efficiency.
Finally, avoid inconsistent data collection methods across shifts or teams. If one team logs every stoppage while another logs only significant ones, your OEE score becomes inconsistent and unreliable. Standardizing data collection methods—ideally with automated tracking systems—keeps your OEE score valid and makes comparisons over time meaningful.
Strategies to Improve OEE
Improving OEE is about more than addressing production bottlenecks specific to a particular industry or process; it’s about creating a proactive approach to efficiency. Implementing a few proven strategies can make a significant impact on availability, performance, and quality, ultimately driving a higher OEE score.
Real-Time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring through Industrial IoT (IIoT) tools, for example, transforms raw manufacturing metrics into actionable insights. By connecting sensors to track machine performance, speed, and quality, operators gain instant visibility into production. Any deviation or anomaly is flagged immediately, allowing teams to act fast and reduce downtime, which improves equipment availability and performance metrics.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance is essential for avoiding unplanned production downtime. By scheduling regular check-ups and maintenance for machines, companies can address wear-and-tear issues before they cause breakdowns. This approach keeps availability high, as production machinery is less likely to stop unexpectedly, allowing the operation to run smoothly.
Predictive Maintenance
Taking it a step further, predictive maintenance uses advanced analytics and machine learning to forecast potential failures. By analyzing machine data, predictive maintenance can alert teams to impending issues, enabling them to make repairs before equipment failure arises. This predictive approach helps maintain high equipment performance by reducing interruptions caused by equipment failures and ultimatelly boost your mean time between failure (MTBF), a key maintenance metric.
Employee Training and Engagement
A well-trained team is essential to maintaining efficiency on the production floor. Regular training helps operators stay proficient with equipment and ensures they know how to respond to unexpected issues. Engaged employees are also more likely to take initiative in reporting inefficiencies and identifying areas for improvement, which benefits all three components of OEE.
Continuous Improvement Programs
Finally, adopting a culture of continuous improvement encourages ongoing efforts to optimize processes. Lean methodologies are valuable tools for identifying waste, reducing variability, and ensuring consistent quality. Continuous improvement doesn’t just boost the OEE score—it builds a resilient production process that evolves with each new challenge.
FAQ
What does OEE mean?
OEE, or Overall Equipment Effectiveness, is a metric used to measure the efficiency of manufacturing operations. It evaluates how effectively equipment is utilized by combining three key factors: availability (how often machines are running), performance (how fast they operate compared to their maximum capacity), and quality (the percentage of products that meet quality standards). OEE provides a clear, actionable insight into productivity, helping manufacturers identify and address inefficiencies to optimize operations.
What does 85% OEE mean?
An OEE score of 85% is widely regarded as the benchmark for world-class manufacturing performance. It means that 85% of the total scheduled production time is being used effectively, with minimal losses in availability, performance, or quality. Specifically, it indicates that equipment is running smoothly with minimal downtime, operating near its maximum speed, and producing high-quality outputs. Achieving this level demonstrates a well-optimized production process with room for only minor improvements.
What are the three components of OEE?
OEE is built on three key components: availability, performance, and quality. Availability measures how often equipment is running during scheduled production time, accounting for unplanned downtime. Performance evaluates how efficiently machines operate compared to their maximum capacity, highlighting speed losses. Quality tracks the percentage of products that meet standards, identifying defects and rework. Together, these components provide a comprehensive view of production efficiency.
How do you calculate OEE?
OEE is calculated by multiplying three key metrics: availability, performance, and quality, expressed as percentages.
- Availability = (Run Time / Planned Production Time) × 100
- Performance = (Run Rate / Ideal Run Rate) × 100
- Quality = (Good Parts / Total Parts) × 100
The formula is:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
The result is a single percentage that reflects how efficiently equipment is being utilized, helping you identify areas for improvement.
What are common mistakes in OEE measuring?
Common mistakes in OEE measurement include misclassifying downtime, such as counting planned maintenance as unplanned downtime, which skews availability. Inaccurate performance tracking is another issue, often caused by overlooking speed losses or minor stoppages. Failing to account for all defective products, including those reworked later, leads to misleading quality metrics. Inconsistent data collection methods between teams or shifts can also result in unreliable OEE scores. Standardizing data collection and leveraging automated systems can help avoid these errors and ensure accurate OEE measurement.
What is OEE KPI?
OEE KPI (Key Performance Indicator) is a metric used to evaluate the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing equipment. It combines three factors: availability (machine uptime), performance (operating speed vs. ideal speed), and quality (percentage of good products). By providing a single, actionable percentage, OEE KPI helps manufacturers identify inefficiencies, reduce downtime, and improve overall production effectiveness.
What does the acronym OEE stand for?
OEE stands for Overall Equipment Effectiveness. It is a key metric used in manufacturing to measure how effectively equipment is utilized by analyzing three components: availability, performance, and quality.
What are OEE benchmarks?
OEE benchmarks are standards used to evaluate the efficiency of manufacturing operations. Generally, a score of 85% is considered world-class, indicating optimal availability, performance, and quality. A score of 50-60% is common for most facilities and signals room for improvement, while anything below 50% often highlights significant inefficiencies. These benchmarks help manufacturers set realistic goals and measure progress toward achieving higher productivity.
How do you measure OEE in real time?
Real-time OEE measurement uses sensors, IIoT tools, and connected devices to track the three components of OEE: availability, performance, and quality. Availability is monitored by tracking machine uptime with tools like current or vibration sensors. Performance is measured through production counters or PLC data to ensure equipment is operating at optimal speed. Quality is assessed using technologies like smart vision systems or defect sensors to identify and log defective products instantly. All this data is processed and displayed in real-time dashboards, enabling quick decisions and immediate action to address inefficiencies.
What are some strategies to improve OEE?
To improve OEE, focus on strategies like real-time monitoring with IIoT tools to instantly detect inefficiencies. Implement preventive maintenance to minimize unexpected downtime and predictive maintenance to address potential failures before they occur. Streamline changeover processes to reduce downtime during product switches and invest in employee training to ensure operators can manage equipment effectively.
